Outline of the Article
- Introduction to River Narmada
- Historical Significance
- Ancient Civilizations along the River
- Cultural Importance
- Geographical Features
- Origin and Course
- Tributaries
- Ecological Importance
- Biodiversity
- Conservation Efforts
- Economic Significance
- Agriculture
- Hydropower
- Religious and Spiritual Importance
- Rituals and Festivals
- Pilgrimage Sites
- Challenges and Threats
- Pollution
- Dams and Deforestation
- Future Prospects
- Sustainable Development Initiatives
- Government Policies
- Conclusion
Article on River Narmada
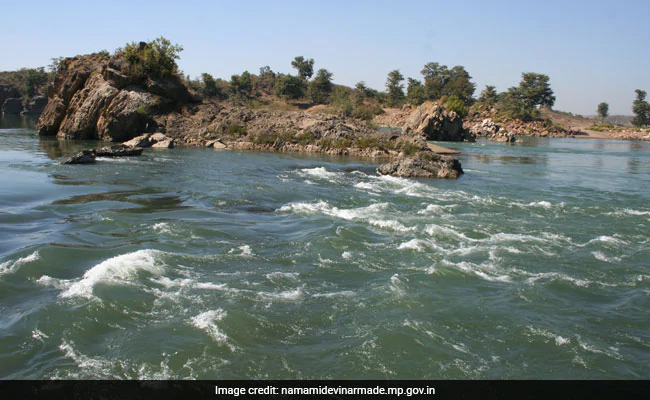
The River Narmada, often referred to as the lifeline of central India, holds a significant place in the hearts of millions. Its journey from the Amarkantak Plateau to the Arabian Sea traverses through diverse landscapes, cultures, and ecosystems, making it a subject of fascination and reverence. Let’s embark on a journey to explore the wonders and intricacies of this majestic river.
Historical Significance
Ancient Civilizations along the River
Since ancient times, the banks of the Narmada have been inhabited by various civilizations, including the Indus Valley civilization and the Vedic civilization. Its fertile plains and abundant water resources have sustained human settlements for millennia.
Cultural Importance
The cultural essence of India is intricately woven with the River Narmada’s presence. It finds mention in numerous mythological texts and scriptures, symbolizing purity and divinity. The Narmada Parikrama, a pilgrimage circumambulating the entire river, is considered highly auspicious by devotees.
Geographical Features
Origin and Course
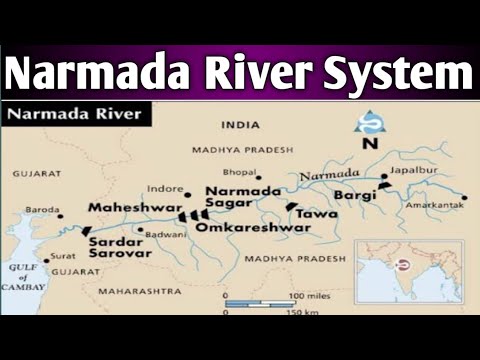
The Narmada originates at Amarkantak, Madhya Pradesh, from the Maikal Range. It flows westward through Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Gujarat, covering a distance of over 1,300 kilometers before draining into the Arabian Sea.
Tributaries
Several tributaries, including the Tawa, Barna, and Hiran, contribute to the Narmada’s flow, enriching its waters and supporting diverse ecosystems along its banks.
Ecological Importance
Biodiversity
The Narmada basin harbors rich biodiversity, including a variety of flora and fauna. The river supports numerous endemic species and provides crucial habitat for several threatened and endangered species.
Conservation Efforts
Efforts are underway to conserve and restore the ecological balance of the Narmada river basin. Conservation organizations and government agencies are working together to implement sustainable management practices and mitigate the impacts of human activities on the river ecosystem.
Economic Significance
Agriculture
The fertile plains of the Narmada basin support extensive agriculture, with farmers relying on the river’s waters for irrigation. Crops such as wheat, rice, and cotton thrive in this region, contributing significantly to the agricultural economy of central India.
Hydropower
The Narmada also plays a vital role in the generation of hydroelectric power. Dams and reservoirs built along its course harness the river’s energy, providing electricity to millions of households and industries.
Religious and Spiritual Importance
Rituals and Festivals
Various rituals and festivals are associated with the River Narmada, reflecting its sacred status in Hindu mythology. Devotees perform ablutions and offer prayers on its banks, seeking blessings and spiritual purification.
Pilgrimage Sites
Numerous pilgrimage sites dot the banks of the Narmada, attracting thousands of devotees each year. From the holy town of Maheshwar to the ancient temples at Omkareshwar, these sacred sites hold immense religious significance.
Challenges and Threats
Pollution
Despite its cultural and ecological significance, the Narmada faces numerous threats, including pollution from industrial effluents, agricultural runoff, and domestic waste. Efforts to control pollution and promote sustainable practices are essential to safeguard the river’s health.
Dams and Deforestation
The construction of dams and deforestation along the Narmada basin have led to habitat destruction, loss of biodiversity, and disruptions to natural ecosystems. Balancing development with environmental conservation is crucial to ensure the long-term sustainability of the river.
Future Prospects
Sustainable Development Initiatives
There is growing recognition of the need for sustainable development along the Narmada basin. Initiatives such as afforestation, watershed management, and community-based conservation projects are being implemented to promote environmental sustainability and improve livelihoods.
Government Policies
Government policies aimed at river rejuvenation and ecosystem restoration are crucial for the future health of the Narmada. Integrated water resource management, pollution control measures, and conservation regulations play a vital role in ensuring the river’s well-being.

Conclusion
In conclusion, the River Narmada embodies the cultural, ecological, and economic wealth of central India. Its journey symbolises the interplay between human civilisation and the natural world, reminding us of the delicate balance that sustains life on Earth. As stewards of this precious resource, it is our collective responsibility to protect and preserve the Narmada for future generations to cherish and enjoy.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- What is the significance of the Narmada river in Hindu mythology?The Narmada river is considered one of the holiest rivers in Hinduism, believed to have originated from the sweat of Lord Shiva.
- How long is the River Narmada?The Narmada river stretches over a length of approximately 1,300 kilometers from its origin to its confluence with the Arabian Sea.
- What are some major tributaries of the Narmada?Major tributaries of the Narmada include the Tawa, Barna, and Hiran rivers.
- What are the primary threats to the Narmada river ecosystem?Pollution from industrial and agricultural sources, as well as habitat destruction due to dams and deforestation, pose significant threats to the Narmada river ecosystem.
- Are there any ongoing conservation efforts for the Narmada river?Yes, various conservation organisation and government agencies are implementing measures to conserve and restore the ecological balance of the Narmada river basin
F*ckin’ awesome issues here. I’m very glad to see your post. Thank you so much and i’m taking a look forward to touch you. Will you kindly drop me a e-mail?
This is the right site for anyone who hopes to understand this topic. You understand a whole lot its almost hard to argue with you (not that I really would want to…HaHa). You certainly put a new spin on a subject that has been discussed for ages. Great stuff, just wonderful!